

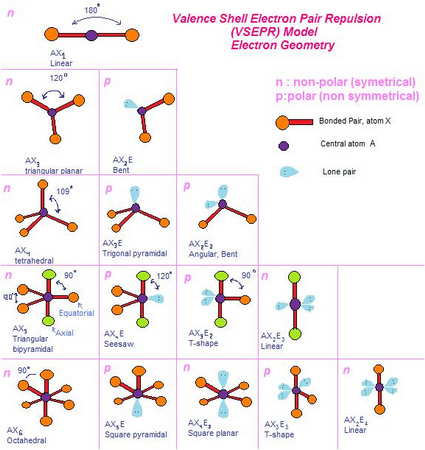
Understanding the principles of electron pair behaviour within a molecule, as shown through Lewis structures, is essential to grasp the fundamentals of VSEPR theory. This theory explains why certain molecules have particular 3D shapes and can help to predict the shape of a molecule based on 2D representations. The acronym VSEPR stands for Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory. The VSEPR theory is a crucial concept in chemistry that defines the shape of molecules based on the repulsion of electron pairs and the presence of bonds.
It's amazing how a simple theory can have such a big impact on our understanding of the world around us. This mathematical theory has allowed us to better understand how molecules and compounds interact and behave with each other. Through rigorous testing and experimentation, VSEPR theory was confirmed as an accurate way to explain the shape of molecules.
#Vsepr theory full
The theory was first proposed by Sidgwick and Powell in 1940, and later expanded upon by Ronald Gillespie and Sir Ronald Nyholm in 1957, who developed it into a full area of theoretical chemistry. In fact, it was developed by many renowned scientists over time. It is important to note that VSEPR theory was not the work of a single scientist. So let's get started! Who proposed VSEPR theory? By the end of this article, you'll have a solid understanding of VSEPR theory and how it applies to the real world. But VSEPR theory isn't perfect - there are some assumptions and inconsistencies to be aware of, like how lone pairs of electrons can affect the overall shape of a molecule. We'll also cover the different molecular geometries that can come from having two, three, four, five, or six electron groups. These help us understand how electrons are arranged in a molecule. One of the key concepts in VSEPR theory is something called Lewis structures. It was first proposed by a scientist named Gillespie, and it's been a big deal in chemistry ever since. To start, VSEPR theory is all about how molecules behave in 3D space. We'll also explore how it's used in real life with some cool examples. The double or triple bond is considered as one electron pair.Let's dive into the fascinating world of VSEPR theory! In this article, we'll explain what it is and who came up with it. Hence repulsion between bond pairs and bond angle decreases.Ĥ. As the electronegativity of the central atom increases,the bond pairs of electrons are pulled more towards the central atom due to which repulsion between bond pairs increase and hence bond angle increases.Īs the electronegativity of atoms bonded to central atoms increases the bond pairs of electrons are pulled towards electronegative atoms.


Principles of VSEPR theory, its definition, some examples, limitations, and advantages of it have been discussed in this blog.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
